1.醫用材料表面工程化;
采用層層自組裝技術,在生物材料表面構建具有多功能、多響應型的納米涂層,實現植入性納米材料的防止炎癥感染,促進組織愈合以及生物相容性。
實例1:多功能納米載藥涂層的構建
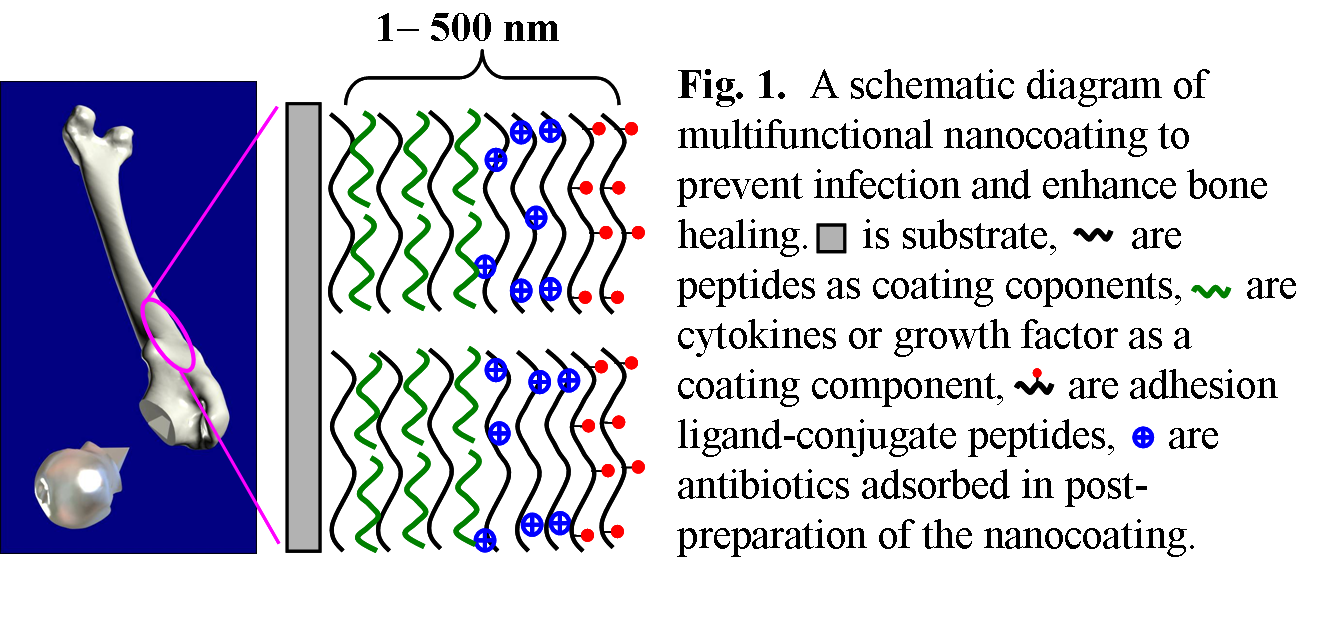
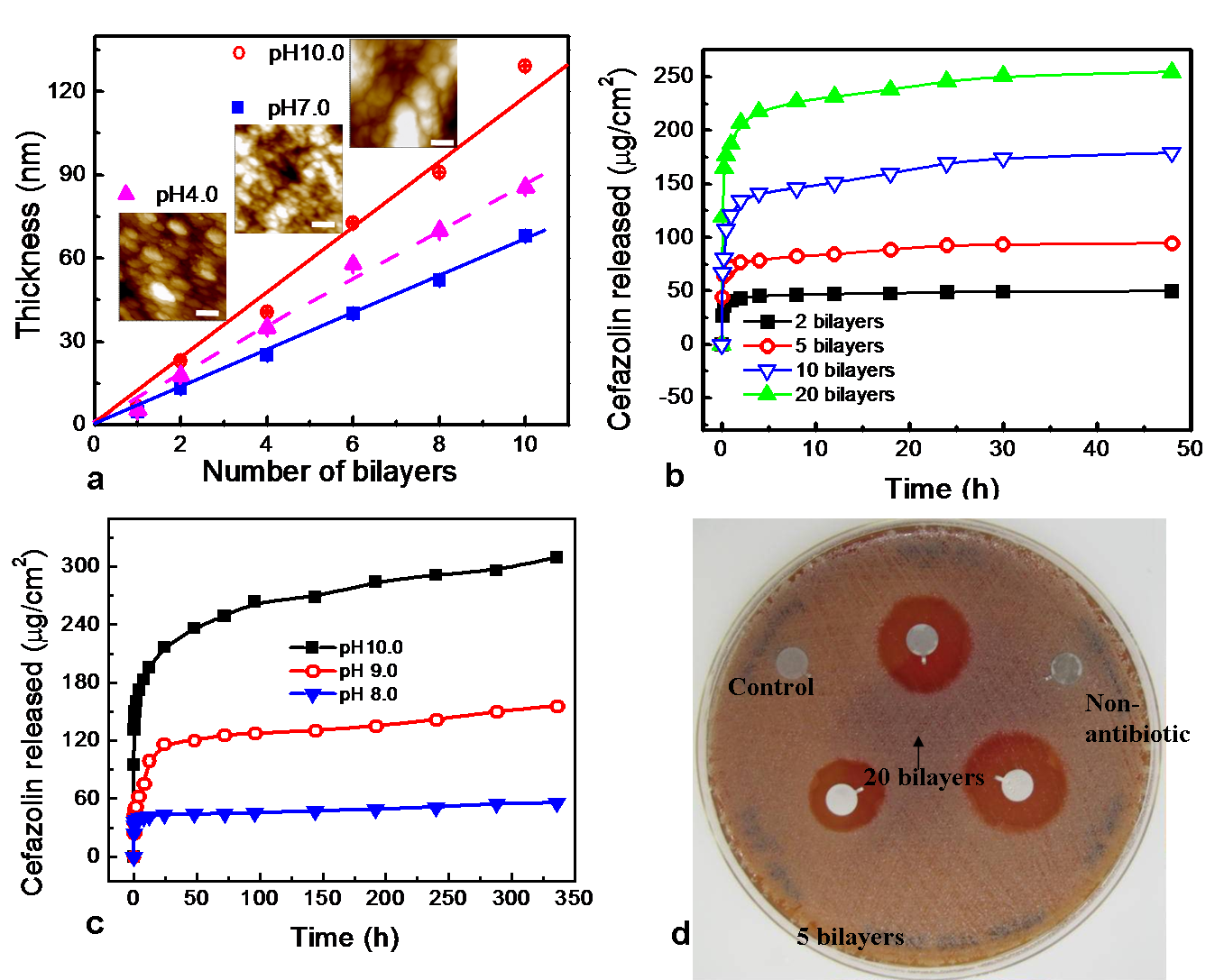
Fig.2. Tunable drug loading and releasing from anti-infection peptide nanocoatings. (a) Nanoassembly with nano-scale structure; (b) Controllable antibiotic incorporation; (c) Tunable releasing of antibiotics; (d) Anti-bacterial activity with Kirby-Bauer assays.
實例2:具有仿生結構的生物涂層的構建
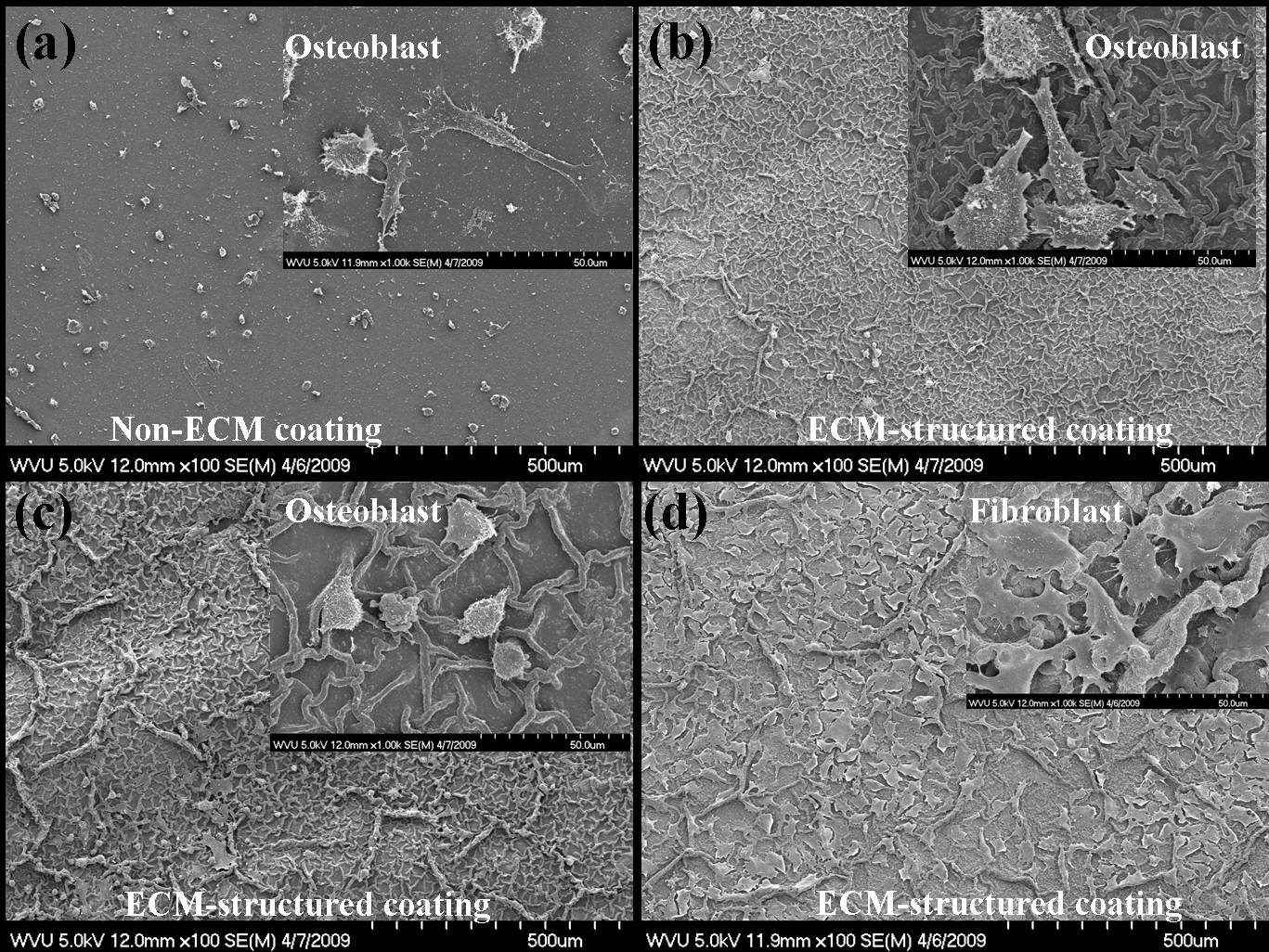
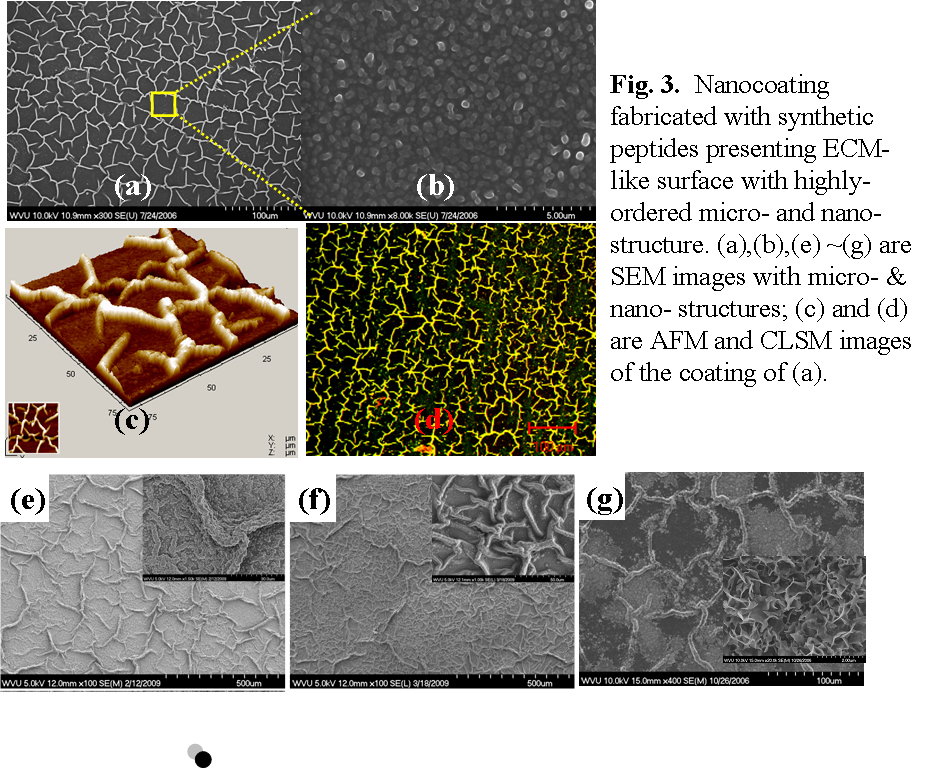

Fig.4. SEM images showed cell adhesion behaviors on ECM-like nanocoating surface. (a)—(c) were the osteoblast adeshision on peptide nanocoating with/without ECM-like structure. (d) was fibroblast adhesion on the same coating as that in (c).
2. 納米給藥;
可生物相容、降解的離子高分子分子設計、合成、藥物載體的組裝行為及其定向傳遞.
實例1:納米粒子的細胞定向傳遞
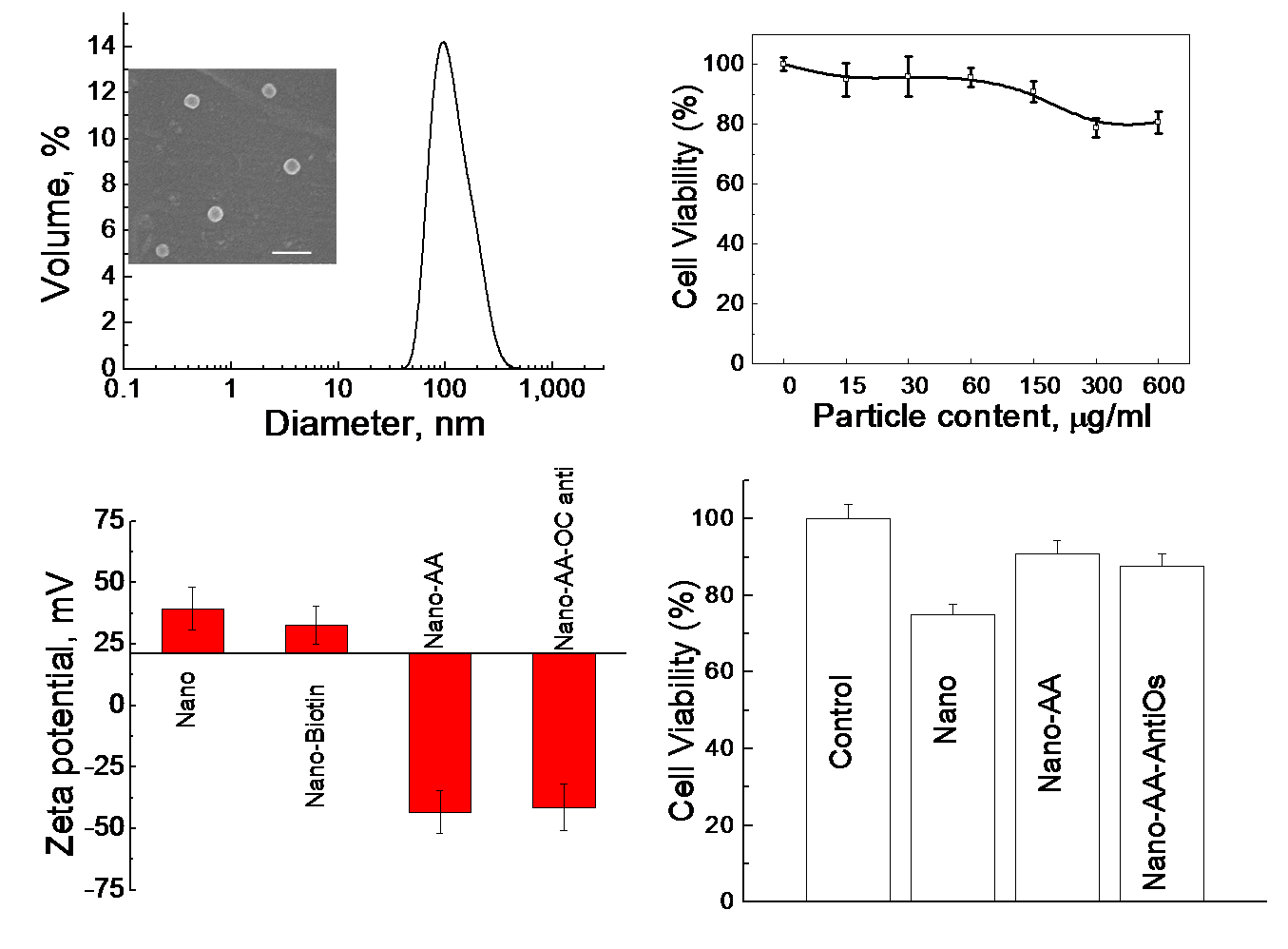
Fig.5 Particle size, zeta potential and morphology and cell cytotoxicity of PEI-grafted PLGA nanoparticles and the surface-modified nanoparticles

Fig.5 Association of surface-modified nanoparticles with osteoblast cells and their intracellular delivery into cell. The nanoparticles in square areas are immobilized into osteoblast cells. A double-stained method was used to indentify the intracellular location of nanoparticles.
3. 溫室氣體吸附材料
新型CO2吸附材料的分子設計、合成及其液相、固相吸附劑的合成與性能;CO2的吸附與光催化轉化反應器的設計與制備。
實例1. 基于層層自組裝技術的納米層狀吸附劑
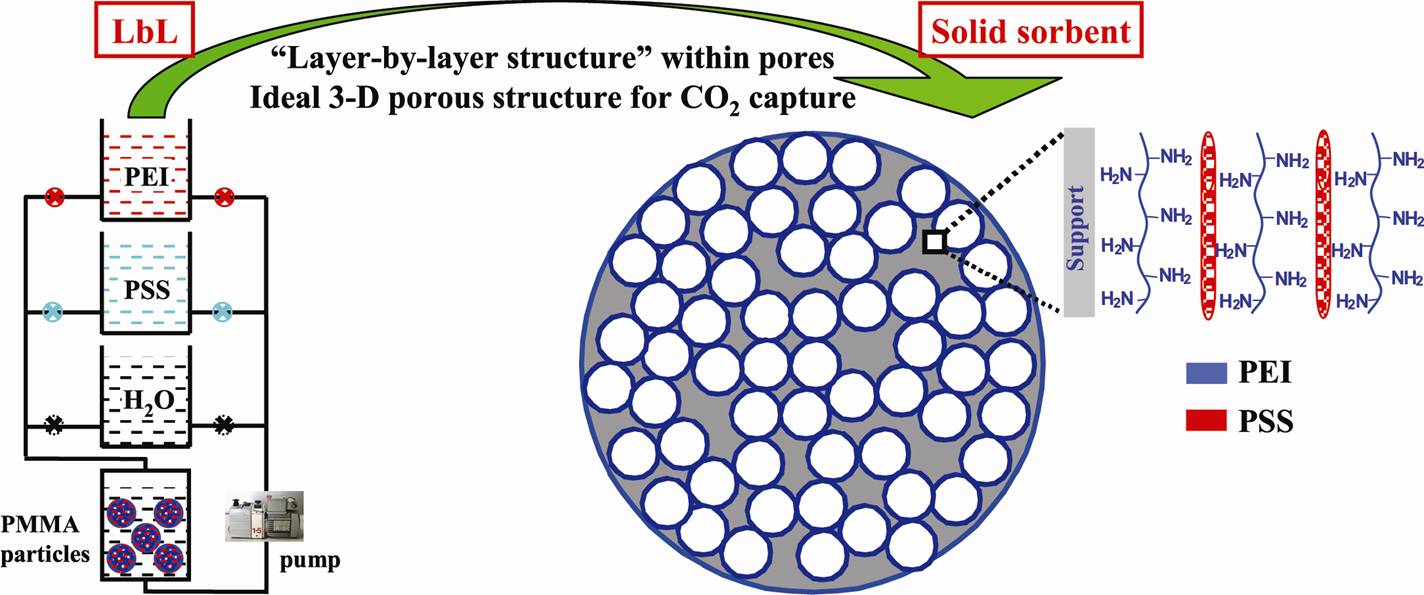
Fig.6 Nanolayered solid sorbents for CO2 capture based on LBL technology
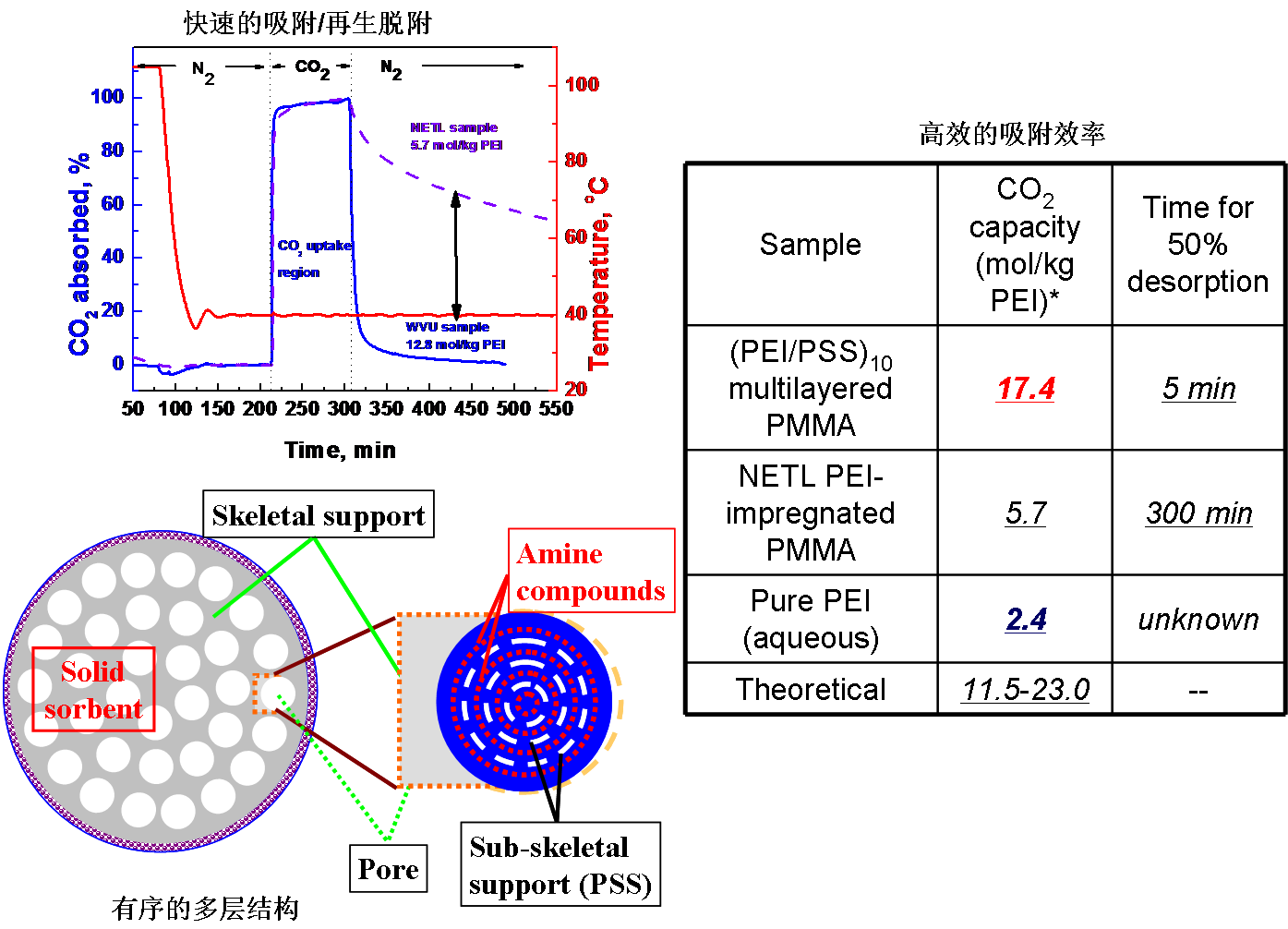
Fig.7 Rapid kinetics(top left) and highly-ordered structure (below left) of nanolayered sorbent and its high amine-efficiency for CO2 capture