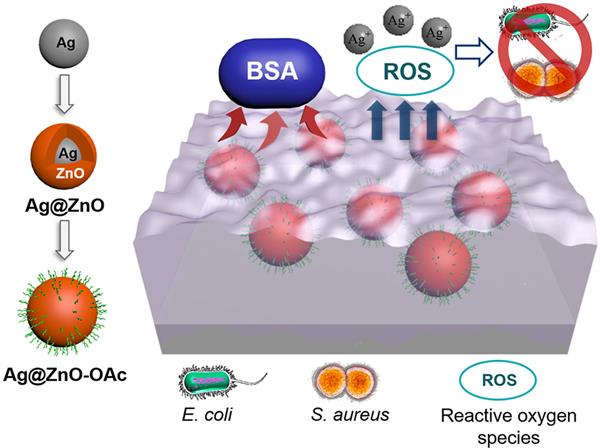
Incorporation of oleic acid-modified Ag@ZnO core-shell nanoparticles into thin film composite membranes for enhanced antifouling and antibacterial properties
writer:Xiujing Huang, Yingbo Chen*, Xianshe Feng, Xiaoyu Hu,Yufeng Zhang, Lei Liu
keywords:Core-shell nanoparticlesThin film nanocomposite membraneAnti-biofoulingAnti-bacterial
source:期刊
specific source:Journal of Membrane Science Volume 602, 1 May 2020, 117956
Issue time:2020年
In this study, Ag@ZnO-Oleic acid (OAc)/polyamide (PA) thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes were prepared by interfacial polymerization with dispersing hydrophobic Ag@ZnO-OAc core-shell nanoparticles in trimesoyl chloride (TMC) solutions. The Ag@ZnO-OAc nanoparticle structure and interactions between OAc and TMC were confirmed by TEM, XPS and FTIR. Surface morphology, roughness, chemical composition, hydrophilicity and charges of the synthesized membranes were characterized by SEM, FTIR, contact angle and zeta potential analyses. The results showed that incorporating the Ag@ZnO-OAc nanoparticles into the PA layer improved chemical and physical properties of the TFN membranes. Compared with the nanoparticle-free TFC membrane, the Ag@ZnO-OAc/PA TFN membrane showed a considerably higher salt rejection, and a lower flux decline rate when tested with filtration of BSA solution as a model foulant and a higher flux recovery with water flush. In addition, the Ag@ZnO-OAc/PA TFN membrane showed excellent antibacterial performance against E. coli and S. aureus.
Highlights
?Hydrophobic Ag@ZnO-OAc NPs were synthesized by microemulsion method.
?Ag@ZnO-OAc NPs reacted with trimesoyl chloride to fabricate TFN membranes.
?Fouling-resistant and antibacterial capacities were effectively integrated.
?Slow and long-term release of Ag+ from Ag@ZnO-OAc NPs in the TFN membranes.