Yixin Han, Xuetao Shi*, Shuangshuang Wang, Kunpeng Ruan, Chuyao Lu, Yongqiang Guo and Junwei Gu*. Nest-like hetero-structured BNNS@SiCnws fillers and significant improvement on thermal conductivities of epoxy composites. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2021, 210: 108666. 2019IF=7.635.(1區(qū)材料科學(xué)Top期刊)
(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108666)
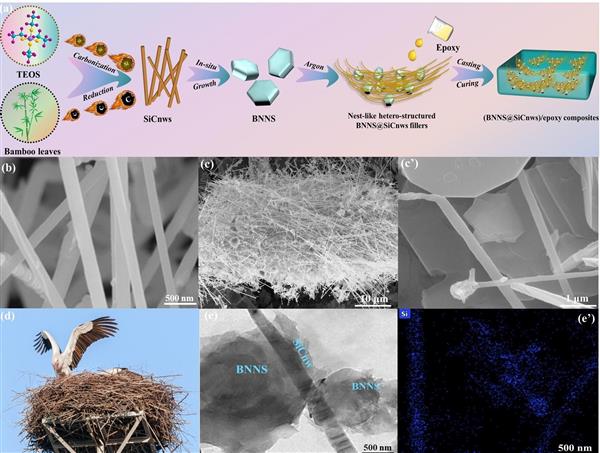
AbstractSilicon carbide nanowires (SiCnws) were in-situ grown on boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) to construct a novel kind of nest-like hetero-structured BNNS@SiCnws thermally conductive fillers from natural bamboo leaves and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) by means of ultrasonic impregnation, sol-gel followed by carbothermic reduction. Then, the thermally conductive & electrically insulating BNNS@SiCnws/epoxy composites were prepared via blending-casting method. When the amount of BNNS@SiCnws-II (65/35, wt/wt) was 20 wt%, BNNS@SiCnws/epoxy composites presented the optimal overall performances. Thermal conductivity coefficient (λ) of BNNS@SiCnws-II (20 wt%) /epoxy composites increased from 0.22 W/mK of pure epoxy matrix to 1.17 W/mK, higher than that of SiCnws/epoxy (0.72 W/mK), BNNS/epoxy (0.82 W/mK) and (BNNS/SiCnws)/epoxy composites (direct mixing BNNS/SiCnws, 65/35, wt/wt 0.76 W/mK) with the same filler concentration of 20 wt%. Meanwhile, BNNS@SiCnws/epoxy composites presented excellent heat transfer/heat dissipation efficiency, due to synergistic effect of the “l(fā)ine-to-surface” hetero-structure of SiCnws and BNNS, which could significantly improve the formation probability of the thermally conductive paths. Furthermore, the BNNS@SiCnws/epoxy composites possessed favorable electrical insulation, thermostability and ideal mechanical properties. Furthermore, the related surface & volume resistivities, the electric breakdown strength, the glass-transition temperature, the heat resistant index, the flexural strength as well as the impact strength of BNNS@SiCnws-II (20 wt%)/epoxy composites reached to be 3.7×1015 Ω, 5.17×1015 Ω·cm, 22.1 kV/mm, 126.7 oC, 185.5 oC, 75.7 MPa and 8.2 kJ/m2, respectively.
本文以天然竹葉為生物質(zhì)碳源結(jié)合正硅酸乙酯(TEOS,硅源),通過超聲浸漬-溶膠凝膠-碳熱還原法在氮化硼納米片(BNNS)上原位生長碳化硅納米線(SiCnws)構(gòu)筑制備“鳥巢狀”異質(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu)BNNS@SiCnws導(dǎo)熱絕緣填料,進(jìn)而與環(huán)氧樹脂基體共混復(fù)合-澆注成型制備BNNS@SiCnws/環(huán)氧樹脂導(dǎo)熱絕緣復(fù)合材料。結(jié)果表明,當(dāng)BNNS@SiCnws-II質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù)為20 wt%時,BNNS@SiCnws-II/環(huán)氧樹脂導(dǎo)熱絕緣復(fù)合材料具有最佳的綜合性能。其熱導(dǎo)率(λ)從純環(huán)氧樹脂的0.22 W/mK提升到1.17 W/mK,均高于相同質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù)(20 wt%)的SiCnws/epoxy(單一SiCnws,0.72 W/mK)、BNNS/epoxy(單一BNNS,0.82 W/mK)和(SiCnws/BNNS)/epoxy(直接共混復(fù)合SiCnws和BNNS,0.76 W/mK)導(dǎo)熱絕緣復(fù)合材料的熱導(dǎo)率,且具有優(yōu)越的傳熱/散熱效能,主要?dú)w因于BNNS@SiCnws-II能充分發(fā)揮SiCnws和BNNS“線-面”異質(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu)的協(xié)同作用,顯著提升導(dǎo)熱通路的形成概率。此時BNNS@SiCnws-II/環(huán)氧樹脂導(dǎo)熱絕緣復(fù)合材料具有優(yōu)異的電絕緣性能、熱穩(wěn)定性以及理想的力學(xué)性能,其表面電阻率(ρs)、體積電阻率(ρv)、電擊穿強(qiáng)度(Eb)、玻璃化轉(zhuǎn)變溫度(Tg)、耐熱指數(shù)(THRI)、彎曲強(qiáng)度和沖擊強(qiáng)度分別為3.7×1015 Ω、5.17×1015 Ω·cm、22.1 kV/mm、126.7oC、185.5oC、75.7 MPa和8.2 kJ/m2。