Review on Chitosan and Two-Dimensional MoS2-Based Proton Exchange Membrane for Fuel Cell Application: Advances and Perspectives
writer:Saad Ahmed, Zhengyuan Tao, Hao Zhang,Muhammad Hassan,Naveed Ahmed,Muhammad Tariq Javid, Jianli Wang
keywords:Chitosan, polymer electrolyte membrane
source:期刊
specific source:energy&fuels
Issue time:2023年
殼聚糖是一種天然多糖,具有豐富的生物量資源,因其獨特的理化性質而引起人們的關注。殼聚糖的重要性最近有所上升(a)因為它是一種可再生和可生物降解的材料(b)因為它有形成膜的能力。因此,殼聚糖是綠色能源應用的首選。本文介紹了殼聚糖化學的最新進展,重點介紹了磺化、磷酸化、鄰苯二酰化和化學交聯等元素修飾反應。然而,基于殼聚糖(CS)的聚合物電解質膜(PEM)的主要問題是如何獲得高質子導電性、跨燃料電池的泄漏和耐久性。為了克服上述問題,殼聚糖和新興的一類無機材料二維過渡金屬二鹵屬化合物,特別是MoS2可用于質子交換膜燃料電池的應用。MoS2的表面功能化為CS/MoS2復合膜的制備開辟了新的途徑。目前的研究還集中在以下幾個方面:(a) PEM的開發策略;(b)殼聚糖在燃料電池應用中的性質和結構;(c)殼聚糖在燃料電池不同部位的應用。本研究還討論了殼聚糖基質子交換膜面臨的進展和特殊挑戰。并詳細討論了控制這些問題的策略和未來的發展方向。
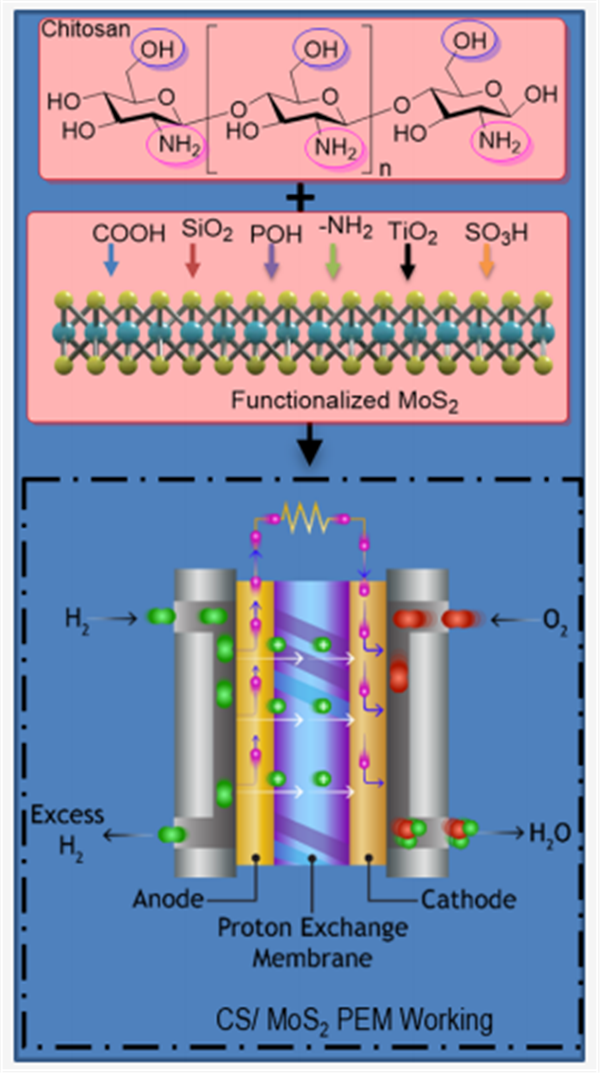
Chitosan is a naturally occurring polysaccharide with abundant biomass resources that attracts interest due to its unique physicochemical properties. The importance of chitosan has risen recently (a) because it is a renewable and biodegradable material and (b) because it has the ability to form a membrane. Therefore, chitosan is highly preferable for green energy applications. This review describes the most recent advancements in chitosan chemistry, emphasizing elemental modifying reactions like sulfonation, phosphorylation, phthaloylation, and chemical cross-linking. However, the major issues of the chitosan (CS)-based polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) are attaining high proton conductivity, leakage across fuel cells, and durability. To overcome the above-mentioned issues, chitosan and the emerging class of inorganic materials 2-D transition metal dichalcogenides especially MoS2 can be employed for proton-exchange membrane fuel cell applications. Surface functionalization of MoS2 can open new pathways for fabricating CS/MoS2 composite membranes. Current research also focuses on the following issues: (a) strategies for the development of PEM, (b) properties and structures of chitosan for fuel cell applications, and (c) chitosan utilization in different parts of the fuel cell. The present study also discusses progress and particular challenges that chitosan-based proton exchange membranes face. Moreover, strategies to control those issues and future aspects are discussed in detail.
本研究由國家自然科學基金(22178317和22109138)、中國博士后科學基金(2020M671790)、中國高等教育委員會和巴基斯坦(Ref. No. 527/ IPFP-II(Batch-I)/SRGP/NAHE/HEC/2020/275)資助。