1.研究背景
近日,上海先進(jìn)熱功能材料工程技術(shù)研究中心于偉教授團(tuán)隊(duì)在Desalination(脫鹽和海水淡化領(lǐng)域的國(guó)際知名期刊,IF=11.211)上發(fā)表了題為“Novel solar membrane distillation system based on Ti?C?T? MXene nanofluids with high photothermal conversion efficiency”的研究論文,將納米流體的光熱效應(yīng)與膜蒸餾系統(tǒng)耦合,大幅提高了直接太陽(yáng)能加熱膜蒸餾系統(tǒng)的水蒸發(fā)效率(提升90%)。該論文是以上海第二工業(yè)大學(xué)能源與材料學(xué)院為第一單位,碩士研究生蔣港凱為第一作者,上海第二工業(yè)大學(xué)高級(jí)工程師雷暉老師為通訊作者。
2.圖文摘要
膜蒸餾(MD)技術(shù)作為一種新的脫鹽工藝,它有效地結(jié)合了熱處理和膜分離,并且由于其操作溫度和壓力要求較低,展現(xiàn)出巨大的商業(yè)應(yīng)用潛力。同時(shí),它也可以和太陽(yáng)能結(jié)合構(gòu)成太陽(yáng)能膜蒸餾(SMD),利用太陽(yáng)能來(lái)進(jìn)一步節(jié)約傳統(tǒng)化石能源的消耗。然而,SMD的光熱轉(zhuǎn)換效率很低,在系統(tǒng)的簡(jiǎn)單設(shè)計(jì)和高效率方面仍然是一個(gè)挑戰(zhàn)。在本研究中,我們開(kāi)發(fā)了一種Ti?C?T? MXene光熱轉(zhuǎn)換材料,并將其進(jìn)一步耦合到一個(gè)新型的SMD系統(tǒng)中。在這個(gè)系統(tǒng)中,光熱轉(zhuǎn)換粒子吸收太陽(yáng)光,將太陽(yáng)能轉(zhuǎn)換成熱能來(lái)加熱進(jìn)水端,這樣完全消除了額外的能量輸入。實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果表明,單層Ti?C?T? MXene具有高效的光熱轉(zhuǎn)換性能,該系統(tǒng)的膜通量可以達(dá)到2.375 kg?m?2?h?1,遠(yuǎn)高于先前報(bào)道的大多數(shù)實(shí)驗(yàn)研究的SMD系統(tǒng)膜通量。我們的研究為實(shí)現(xiàn)太陽(yáng)能的高效利用和膜蒸餾海水淡化提供了實(shí)驗(yàn)和理論依據(jù)。

Fig. 1. Preparation flow chart of Ti3C2Tx with different morphologies

Fig. 2. Novel SMD system coupling a new type of photo-thermal conversion material with the membrane distillation system.

Fig. 3. (a) (b) SEM images of the M-MXene. (c) TEM image of the M-MXene sheets. (d) (e) SEM images of the S-MXene. (f) TEM image of the S-MXene sheets. (g) (h) SEM of the TiN. (i) The XRD patterns of MXene and Ti?AlC?.
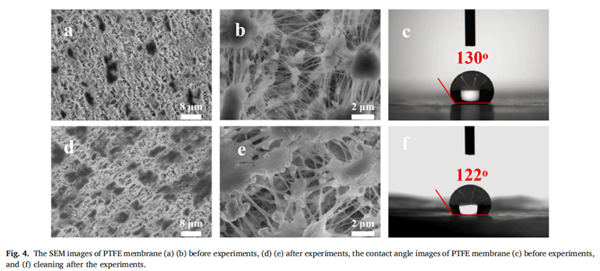
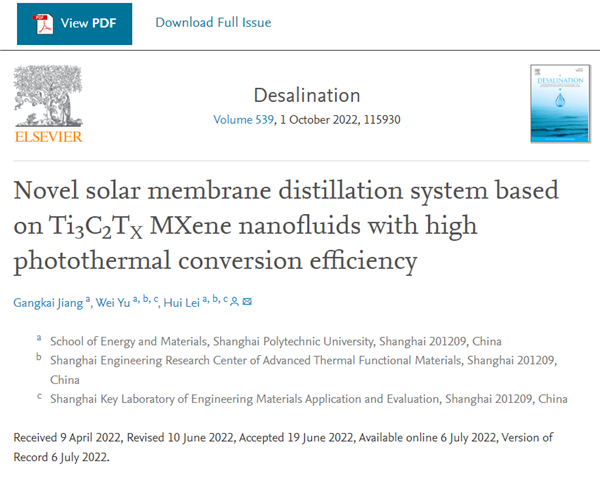
Fig. 4. The SEM images of PTFE membrane (a) (b) before experiments, (d) (e) after experiments, the contact angle images of PTFE membrane (c) before experiments, and (f) cleaning after the experiments.
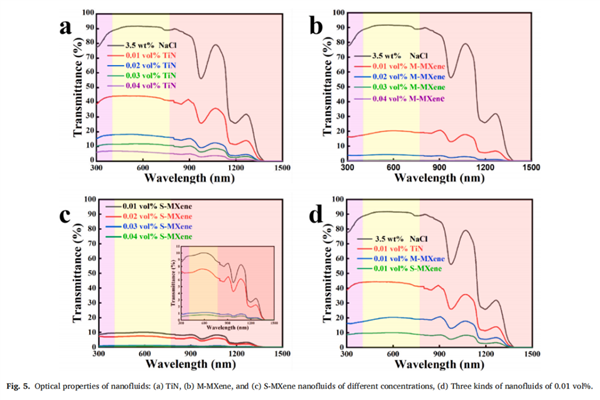
Fig. 5. Optical properties of nanofluids: (a) TiN, (b) M-MXene, and (c) S-MXene nanofluids of different concentrations, (d) Three kinds of nanofluids of 0.01 vol%.
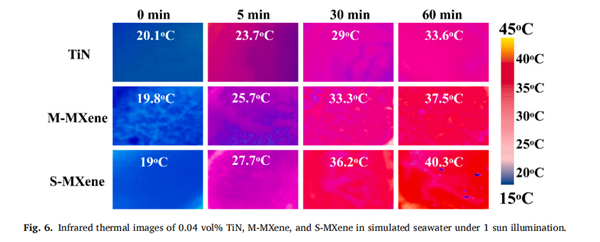
Fig. 6. Infrared thermal images of 0.04 vol% TiN, M-MXene, and S-MXene in simulated seawater under 1 sun illumination.

Fig. 7. Evaporation performance of nanofluids with different volume concentrations: temperature and mass change of (a)(b) TiN nanofluids, (c)(d) M-MXene nanofluids, and (e)(f) S-MXene nanofluids, (g) Temperature comparison of three kinds of nanofluids with 0.04 vol%, (h) evaporation efficiency of three kinds of nanofluids.

Fig. 8. Solar DCMD performance: (a) Five dynamic temperatures of 0.04 vol% S-MXene nanofluids, (b) Mass change of four kinds of nanofluids, (c) The membrane flux of four kinds of nanofluids, (d) Product water conductivity, (e) The membrane flux in the cycle test, (f) Comparison of the evaporation rate between our steam generator and the reported steam generator devices in the literature.
3.小結(jié)
綜上所述,我們提出了一種新型太陽(yáng)能膜蒸餾系統(tǒng),并在實(shí)驗(yàn)室搭建了該系統(tǒng),同時(shí)將光熱轉(zhuǎn)換材料引入到所設(shè)計(jì)的系統(tǒng)中。這項(xiàng)工作從分析當(dāng)前太陽(yáng)能膜蒸餾系統(tǒng)的關(guān)鍵問(wèn)題開(kāi)始,目的是提高太陽(yáng)能光熱利用和海水淡化的效率。同時(shí),通過(guò)利用具有優(yōu)異性能的光熱轉(zhuǎn)換材料,提高了產(chǎn)水率。與傳統(tǒng)的SMD相比,本研究設(shè)計(jì)的復(fù)合系統(tǒng)具有更高的膜通量,達(dá)到2.375 kg?m?2?h?1,并且降低了能源消耗的成本。在未來(lái),可以進(jìn)一步通過(guò)改善系統(tǒng)的隔熱性能,優(yōu)化操作條件(如進(jìn)水速度)和優(yōu)化進(jìn)水流道及導(dǎo)流格網(wǎng)的設(shè)計(jì)等,來(lái)進(jìn)一步提高新型SMD系統(tǒng)的產(chǎn)水率。我們的研究為實(shí)現(xiàn)太陽(yáng)能膜蒸餾提供了實(shí)驗(yàn)和理論基礎(chǔ),這種新型SMD系統(tǒng)在海水淡化和廢水處理中將具有巨大的應(yīng)用潛力。
作者:蔣港凱,于偉教授,雷暉老師
單位:上海第二工業(yè)大學(xué)能源與材料學(xué)院
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.115930