Preparation of robust poly(ε-caprolactone) hollow spheres with controlled biodegradability
writer:Shi, Z. Q.; Zhou, Y. F.; Yan, D. Y.*
keywords:biodegradable;ε-caprolactone;controlled release;crosslinking;hollow spheres;silicas
source:期刊
specific source:Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1265. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/marc.200600307/p
Issue time:2006年
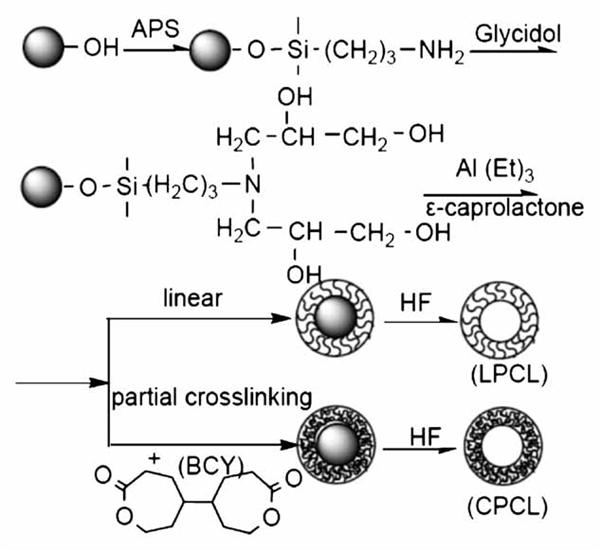
This work reports a new type of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) robust hollow sphere with controllable biodegradability, produced by grafting PCL shells from the surface of silica sphere cores and removing the template cores. Bis(ε-caprolactone-4-yl) (BCY) composed of two ε-caprolactone molecules was used as the crosslinker, which not only greatly strengthened the PCL hollow spheres but also brought hardly any non-biodegradable component into the system. Solubility experiments and biodegradation tests show that the crosslinked PCL hollow spheres were robust both in water and acetone, and were completely biodegradable with characteristics of controllable biodegradability according to the content of the BCY. The Rhodamine release test indicated that the release rate of encapsulated drugs in the PCL hollow spheres was controlled by diffusion and the biodegradability of the PCL molecules, and the latter mechanism will dominate when more enzymes are involved.